Image Pixels Visualizer
So what is a pixel?
A pixel, often abbreviated as px, serves as the fundamental building block in a digitally-displayed image. These tiny units form the basis of a raster, aligning together on a screen to create a cohesive image. Collectively, pixels come together to constitute what is known as a raster image.
Pixels represent the smallest units of information within a digital picture. Commonly taking on round or square shapes, they are organized in a two-dimensional grid, creating the visual structure of the image on a display.
Let's look closer!
In the image below, one portion has been magnified many times over so that you can see its individual composition in pixels. As you can see, the pixels approximate the actual image. The more pixels you have, the more closely the image resembles the original.

© Julie Waterhouse Photography
Resolution
The quantity of pixels in an image is occasionally referred to as 'resolution,' though this usage is somewhat imprecise. When we mention resolution in the context of pixel count, it is common to express it as the width by the height. For instance, a resolution of 1280×1024 signifies that there are 1280 pixels horizontally and 1024 pixels vertically. This format provides a clear representation of the dimensions, indicating the pixel count from side to side and top to bottom.
What are pixels made up of?
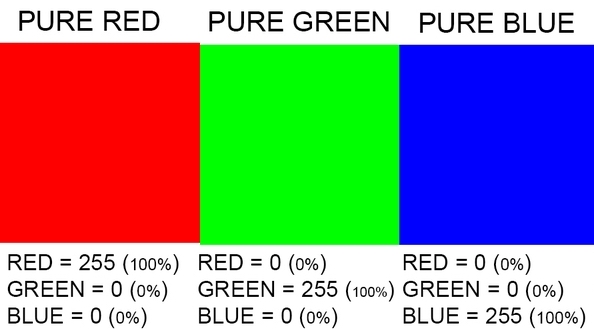
In order for a pixel to represent a specific color, it is composed of subpixels in the colors red, green, and blue (RGB). These subpixels can have different shapes to create a layout with good image definition and few spaces between the pixel elements.
A colored image is composed of multiple colors and all colors can be generated from the three (red, green and blue) colors.
The color range between 0-255 represents the intensity of the color for that pixel.That concept is illustrated here:
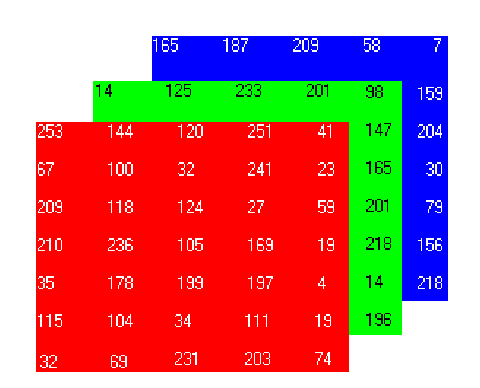
The output color of the individual pixel is a combination of the color values of three subpixels in each case. The three colors are mixed additively and can, in this way, assume different values. Additive mixing means superimposing.
© www.nikonians.org-forums-user_files-376816
If all three primary colors have the maximum value of 255, the output is white. If rgb = (0, 0, 0), black appears. The values in between allow around 16.7 million shades of color (2563) to be displayed. Lighter colours rgb tend to (1, 1, 1) darker colours tend to (0, 0, 0).